Trading chart gaps can be one of the most exciting strategies for traders. These gaps can offer unique insights into market movements, allowing for profitable opportunities when identified and traded correctly. If you’re new to chart gaps or want to refine your gap-trading strategy, this article will guide you through the process from start to finish.
What Are Chart Gaps
Chart gaps are one of the most intriguing phenomena in technical analysis and trading. A chart gap occurs when the price of a security, such as a stock, opens significantly higher or lower than the closing price of the previous day. This price difference results in a visible “gap” on the price chart, hence the name. Gaps are important for traders because they often signal a shift in market sentiment, which can lead to rapid price movements. These gaps are not just limited to daily time frames; they can also appear on weekly, monthly, or even intraday charts, depending on the market’s volatility and the events that influence it.
Chart gaps are not random occurrences. They often result from fundamental or technical factors that cause a surge in buying or selling pressure. For traders, understanding what causes a gap and how to interpret it is crucial for identifying profitable trading opportunities. Gaps can indicate everything from the start of a new trend to the exhaustion of an existing one, making them a versatile tool in a trader’s arsenal.
Why Do Chart Gaps Occur
Chart gaps typically occur when there is a significant imbalance between buyers and sellers, often triggered by unexpected news or major events. These events create sharp changes in supply and demand dynamics, causing the price to “jump” rather than move gradually. For instance, if a company releases a positive earnings report or announces an exciting new product, the increased demand for its stock may lead to a gap up in price. Similarly, negative news, like a poor earnings report or unfavorable regulatory changes, can cause a gap down as traders rush to sell their positions.
Apart from earnings reports, other news events such as mergers, acquisitions, or geopolitical developments can cause chart gaps. Even macroeconomic factors like interest rate decisions or government policy changes can lead to significant gaps. The key point is that gaps occur when the market receives new information that causes traders to quickly reassess the value of a security, leading to a sudden price jump. For traders, being aware of these potential triggers is essential for successful gap trading.
Different Types of Chart Gaps
Chart gaps can be classified into several categories, each with distinct characteristics that provide traders with different insights into market behavior. Below are the four primary types of chart gaps.
Breakaway Gaps
Breakaway gaps are perhaps the most exciting for traders because they signal the beginning of a new trend. These gaps occur when the price “breaks away” from a consolidation phase or a well-established trading range. Often, this type of gap is accompanied by strong volume, reinforcing the validity of the price movement. Traders consider breakaway gaps a sign that the market sentiment has shifted, and a new bullish or bearish trend is likely to form. These gaps are typically seen after periods of indecision, where the market has been trading sideways, and then suddenly experiences a sharp breakout.
Key characteristics of breakaway gaps include:
- Occur at the start of a new trend.
- Are often accompanied by a sharp increase in volume.
- Usually occur after a period of consolidation or range-bound trading.
- Can break through key support or resistance levels.
To identify breakaway gaps, traders should look for a sharp price movement that breaks a major support or resistance level. Volume is a critical confirmation tool, as a gap with low volume might not sustain the move, leading to a potential reversal. Breakaway gaps tend to offer substantial profit opportunities, especially when followed by strong momentum in the direction of the gap.
Runaway Gaps (Continuation Gaps)
Runaway gaps, also known as continuation gaps, occur in the middle of an established trend. These gaps typically indicate that the trend is gaining momentum and will continue in the same direction. Unlike breakaway gaps, which mark the start of a new trend, runaway gaps appear during an ongoing trend and suggest that the current price movement still has room to run. These gaps are often fueled by increasing market participation, with more traders joining the trend as it gains traction.
Key signs of runaway gaps include:
- Appear in the middle of a strong trend.
- Signal that the trend will likely continue.
- Are often caused by increasing market sentiment in the trend’s direction.
- Tend to have moderate volume compared to breakaway gaps.
The market sentiment behind runaway gaps is typically strong. In a bullish trend, investors might rush to buy stocks, believing the trend will continue upward, while in a bearish trend, traders may continue selling, expecting further downside. Traders can use runaway gaps to increase their positions in an ongoing trend or to confirm the trend’s strength. However, it’s essential to be cautious of exhaustion gaps, which might signal the end of the trend (more on that later).
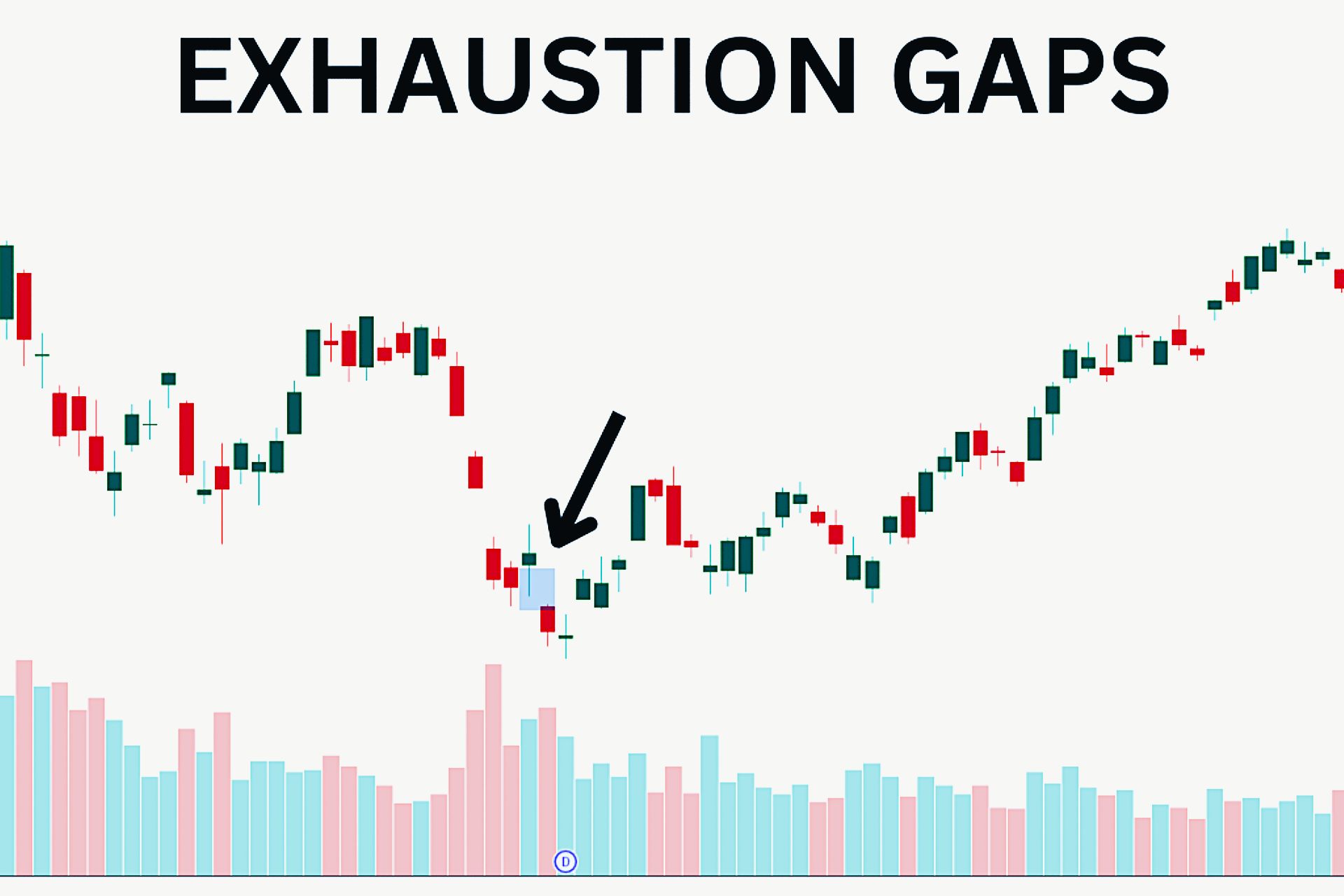
Exhaustion Gaps
Exhaustion gaps are the opposite of runaway gaps, signaling that a trend is coming to an end. These gaps often occur near the end of an extended uptrend or downtrend, and they suggest that the market is “exhausted.” Traders who misinterpret these gaps as continuation signals may find themselves caught on the wrong side of the trade. Exhaustion gaps are often followed by a reversal in the price, as the market loses the strength to continue in the current direction.
Key features of exhaustion gaps include:
- Occur near the end of an extended trend.
- Often have decreasing volume, showing a loss of momentum.
- Are typically followed by a price reversal.
- Signal that the current trend is weakening.
To recognize exhaustion gaps, traders should pay attention to the context in which they occur. If the gap happens after a long price movement and is accompanied by decreasing volume, it may be a sign that the trend is losing steam. Exhaustion gaps can provide excellent opportunities for contrarian traders looking to profit from a reversal.
How to Identify Chart Gaps
Identifying chart gaps is an essential skill for traders looking to capitalize on sudden market movements. Gaps can reveal vital information about the market’s strength or weakness, but correctly identifying them requires careful analysis of various technical factors, including price patterns, volume, and time frames. Below, we’ll explore how to use each of these tools to spot chart gaps effectively.
Analyzing Price Patterns
One of the most straightforward ways to identify chart gaps is by studying price patterns, especially around key levels of support and resistance. Support and resistance levels act as psychological barriers for traders, and when a gap forms through these levels, it can indicate a strong directional move. For instance, if a stock has been trading just below a resistance level and suddenly gaps above it, this could signal a bullish breakout. Similarly, a gap below a support level often points to a bearish continuation.
Price patterns like head and shoulders, flags, or triangles can also help in identifying potential gaps. When these patterns appear at critical junctions on the chart, and a gap occurs, it usually confirms the validity of the pattern. For example, in a bullish flag, a gap up through the resistance of the flag pattern could signal the start of a new upward trend. By combining chart patterns with gap analysis, traders can increase the probability of successful trades.
Using Volume Indicators
Volume is a key factor in confirming the strength and significance of a gap. When a price gap is accompanied by a substantial increase in volume, it suggests that the gap is valid and likely to continue in the direction of the gap. Volume essentially measures the market’s conviction behind a move. If a stock gaps up but on low volume, it could be a false breakout, and the price might soon reverse. However, a gap with strong volume usually indicates that institutional investors are behind the move, increasing the likelihood of a sustained trend.
Using volume indicators such as the Volume Oscillator or On-Balance Volume (OBV) can help in gap trading. These indicators show whether the volume is increasing or decreasing and can be used to confirm the strength of a breakout or breakdown. For instance, if a price gaps up and the OBV rises simultaneously, it suggests that buying pressure is strong, making the gap more reliable. Conversely, if volume declines after a gap, it could indicate a lack of enthusiasm for the move, which might lead to a price reversal.
Time Frames for Spotting Gaps
Gaps can appear on any time frame, but their significance varies depending on the chart period you’re analyzing. Longer time frames, such as daily or weekly charts, tend to provide more reliable gap signals, as these gaps are generally caused by major news or economic events. A daily or weekly gap that breaks through a key level of support or resistance is typically more meaningful than a gap seen on a five-minute intraday chart, as it represents a broader shift in market sentiment.
However, intraday traders can also profit from gaps by focusing on shorter time frames like the 1-hour or 15-minute chart. While gaps on these shorter time frames may not indicate long-term trends, they can present profitable opportunities for quick trades, especially in volatile markets. For swing traders and longer-term investors, focusing on daily or weekly gaps is generally more effective, as these are less likely to be filled quickly and often represent the beginning of major market moves.
| Factor | How It Helps Identify Gaps | Key Indicators | Time Frames |
| Price Patterns | Gaps through support/resistance signal strong moves | Support/Resistance, Triangles, Head and Shoulders | Daily, Weekly, Intraday |
| Volume Indicators | High volume confirms the gap’s strength | Volume Oscillator, OBV | Daily, Weekly |
| Time Frames | Longer time frames provide more reliable gaps for longer trends | 1-hour, Daily, Weekly | Longer-term trends (daily/weekly) |
Trading Strategies for Chart Gaps
Once you’ve identified chart gaps, the next step is developing a trading strategy to capitalize on them. Different types of gaps require unique trading approaches, and it’s essential to understand how to manage risks and maximize profit potential. Below, we’ll dive into two common types of gaps and how to trade them effectively.
Trading Breakaway Gaps
Breakaway gaps mark the beginning of a new trend and provide some of the most profitable trading opportunities. To trade a breakaway gap effectively, it’s crucial to enter the trade as soon as possible after the gap is confirmed. The gap usually occurs after a period of consolidation or range-bound trading, signaling a breakout through a key level of support or resistance. Once this breakout happens, it is often followed by a sharp price movement in the direction of the gap. To reduce risk, traders should place their stop-loss orders just below the gap (for a bullish trade) or above it (for a bearish trade). This helps in limiting potential losses if the gap fills or the price moves against the trade.
In terms of profit-taking, traders should aim for a target based on the strength of the trend and the volatility of the asset. You can use tools like Fibonacci extensions or moving averages to estimate where the price may head after the gap. Another useful strategy is to scale into the trade as the trend strengthens, especially if the gap is accompanied by increasing volume. Trailing stops can also be helpful for locking in profits as the price continues to move in your favor. Proper risk management is crucial when trading breakaway gaps, as they can result in large price movements, both in your favor and against you.
Trading Runaway Gaps
Runaway gaps, also known as continuation gaps, occur within an already established trend and are an indication that the trend is gaining strength. These gaps often happen in the middle of a bullish or bearish trend, and they signal that the market is likely to continue moving in the same direction. The key to trading runaway gaps is to wait for confirmation of the gap. Once the gap is confirmed, traders can enter in the direction of the trend, taking advantage of the momentum behind the move. Since runaway gaps occur during strong trends, they often provide excellent opportunities to add to existing positions.
However, it’s essential to be cautious when trading runaway gaps, as overextending your position can lead to greater risk. To manage this, traders should place their stop-loss orders just below the gap in the case of a bullish trend or just above the gap for a bearish trend. This ensures that if the trend reverses or the gap fills, losses are minimized. Additionally, traders should keep an eye on the overall market sentiment and volume. A runaway gap accompanied by high volume is more likely to sustain its momentum, while a gap with low volume could signal a potential trend exhaustion. By riding the momentum but maintaining a cautious approach, traders can capitalize on runaway gaps while managing their risk effectively.